PSY 164: Sensation and Perception
Class 3
Neurons and their behavior
- The Neural Impulse
- The Resting Potential
- The Resting Potential a. -70 mV
- The Sodium/Potassium Pump
- The Action Potential
- The Voltage Cycle
- All-or-None Law
- All action potentials same size
- Action potential stays sames Size as travels
- How does the action potential happen chemically
- What does this mean?
- Saltatory Conduction
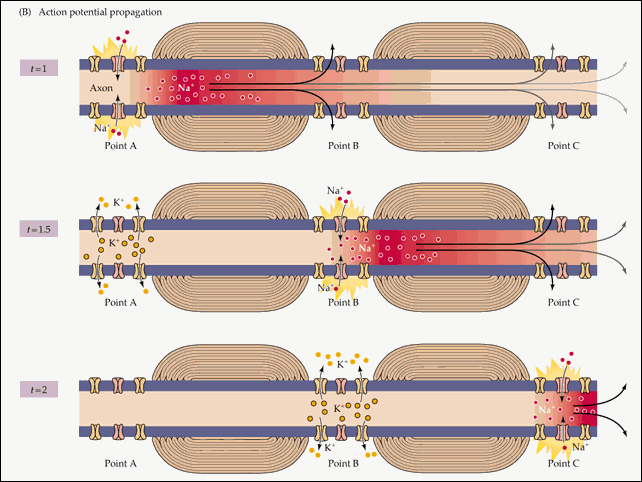
- Refractory Periods
- Absolute :
- Basically Sodium Channel is Open
- Lasts ~ 1 ms
- Relative :
- Rest of action potential till after overshoot is done
- Lasts 1-2 msec
- Synapses
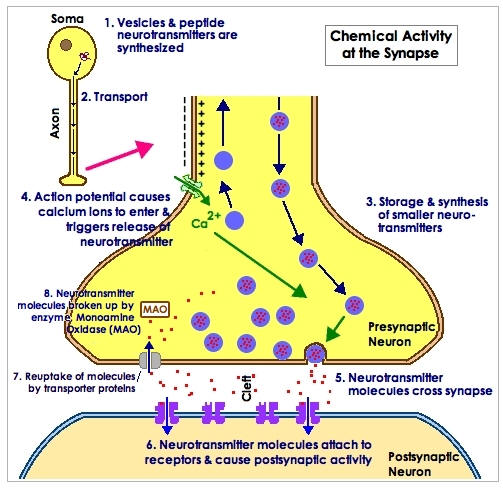
found: http://web.lemoyne.edu/~hevern/psy340/lectures/psy340.03.1.synapse.html
source unknown.
- Synaptic Transmission
- Production
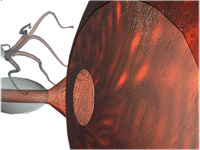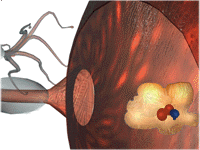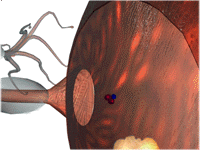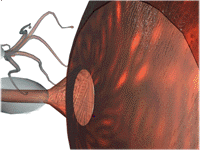
- Storage
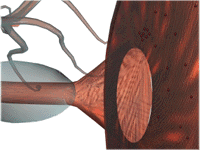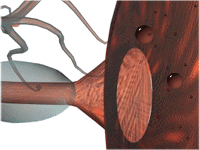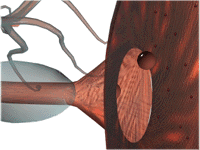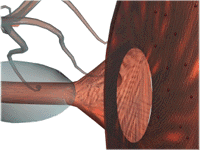
- Release
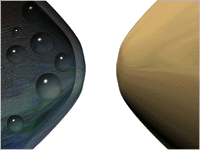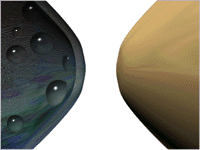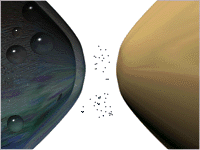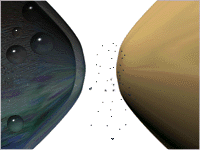
- Binding
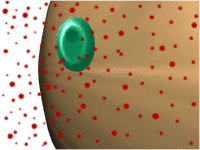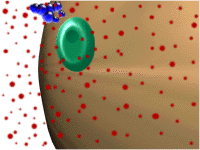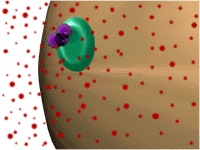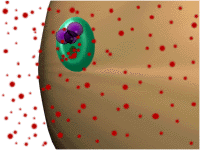
- Removal -
Destruction and Reuptake

From "Action at the Synapse" the
Psychology Place now owned by Pearson Ed.
- Generating a New Action
Potential
- Summation
- Spatial
Summation
- Temporal
Summation
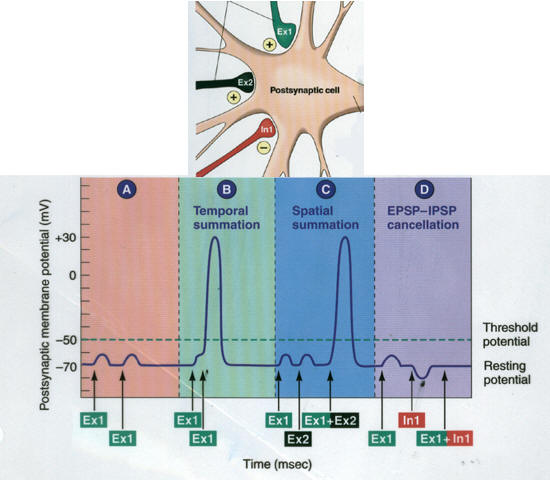
from: http://www.colorado.edu/kines/Class/IPHY3730/04nervephysiology.html
- Let us See Summation in Action
- The Brain
- General Organization
- The Brain is divided
into four lobes
- Frontal
- Parietal
- Temporal
- Occipital
- The Thalamus
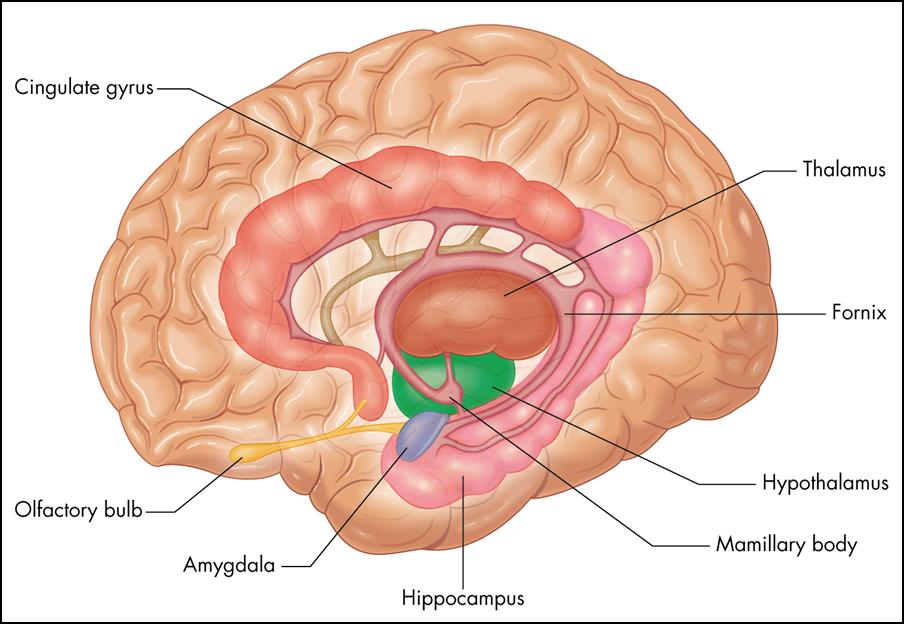
Source unknown
- The Cortex
- Is the surface
of the brain, about 1/4" thick
- Is composed of
6 layers
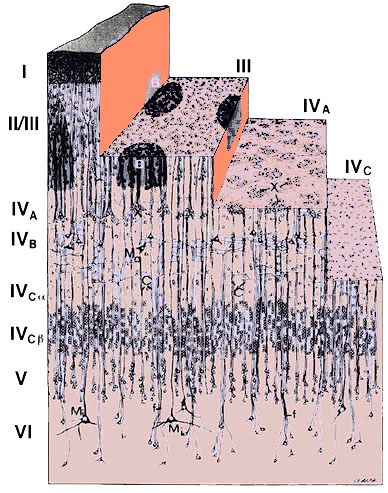 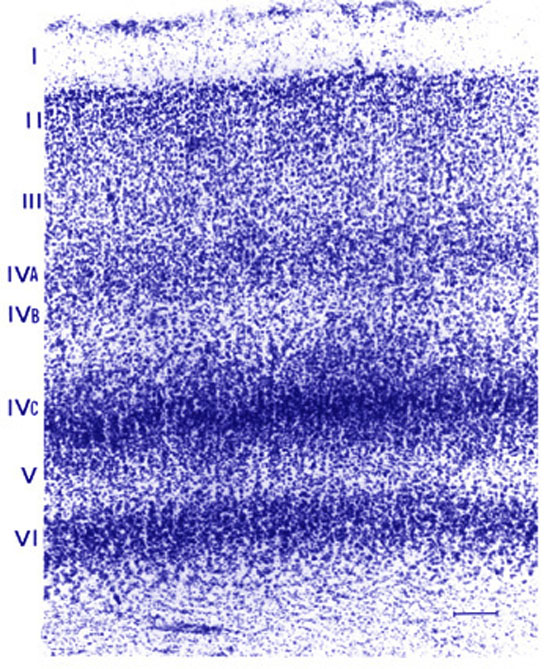
Netter, Ciba Collection of Medical
Illustrations Source unknown
- Different parts of the cortex
perform different functions, e.g.:
- Visual Cortex: Occipital Lobe
- Auditory Cortex: Temporal Lobe
- Somatosensory Cortex: Parietal Lobe:
Postcentral Gyrus
- Motor Cortex: Frontal Lobe: Precentral
Gyrus
|